Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yee-Rendon, B.; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Maekawa, Fujio; Meigo, Shinichiro; Tamura, Jun
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1350(1), p.012120_1 - 012120_5, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:52.28(Physics, Particles & Fields)Yee-Rendon, B.; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Maekawa, Fujio; Meigo, Shinichiro; Tamura, Jun
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1350(1), p.012197_1 - 012197_7, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:73.22(Physics, Particles & Fields)Yee-Rendon, B.; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Maekawa, Fujio; Meigo, Shinichiro; Tamura, Jun
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1350(1), p.012198_1 - 012198_6, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:52.28(Physics, Particles & Fields)Kamiya, Junichiro; Okabe, Kota; Kinsho, Michikazu; Moriya, Katsuhiro; Yamada, Ippei; Ogiwara, Norio*; Hikichi, Yusuke*; Wada, K.*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1350, p.012149_1 - 012149_6, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:82.33(Physics, Particles & Fields)To obtain a getter effect to titanium vacuum duct surface, the method to remove the oxide on the surface by sputtering with ionized molecules has been developed. In the method, a sheet-shaped gas distribution with a uniform and high density is generated through a narrow slit by a small amount of gas. In this report, the gas density distribution was calculated by the Monte Carlo simulation code. As a result, it was found that a gas injection from both directions was effective to generate uniform density distribution. Furthermore, the gas injection method was applied to a non-destructive beam profile monitor, that detects ions generated by the interaction between gas molecules and beam. In this monitor, dependence of the beam profile on the injected gas amount was measured. A small amount of injected gas was found to be ideal for the beam profile measurements in the unsaturated and a high S/N ratio region.
Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Ueno, Tomoaki; Horino, Koki
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1350(1), p.012183_1 - 012183_7, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.06(Physics, Particles & Fields)As one of the advanced research and development for maintaining the stable operation of J-PARC RCS, we are developing semiconductor switch circuit for thyratron substitute adopted in kicker system. Radiation symmetric type circuits using semiconductors of SIC-MOSFETs are composed of circuits in which many semiconductor switches are multiplexed in parallel. Since the lengths of all parallel circuits are equal, the output waveform will not be distorted due to timing jitter or impedance. This circuit is useful for outputting the waveform of ultrafast short pulse. Therefore, we have developed a circuit that achieves further low inductance by making the power transmission circuit into a double circular ring structure equal to the coaxial shape. Compare the inductance value obtained from the structure and the output waveform. In addition, we compare the calculation and the measurement in the test and present the verification result of the developed circular ring structure.
Tamura, Fumihiko; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Sugiyama, Yasuyuki*; Yoshii, Masahito*; Omori, Chihiro*; Shimada, Taihei; Nomura, Masahiro; Hasegawa, Katsushi*; Hara, Keigo*; Furusawa, Masashi*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1350(1), p.012189_1 - 012189_7, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:52.28(Physics, Particles & Fields)Magnetic alloy cavities are employed in the J-PARC RCS to generate high accelerating voltages. The cavity, which is driven by a vacuum tube amplifier, has a wideband frequency response and the beam loading in the cavity is multiharmonic. Therefore, the tube must generate a multiharmonic output current. An LTspice circuit model is developed to analyze the vacuum tube operation and the compensation of the multiharmonic beam loading. The model includes the cavity, tube amplifier, beam current, and LLRF feedback control. The feedback control consists of the I/Q demodulator including low pass filters, PI control, and I/Q modulator. In this presentation, we present the implementation of the LLRF functions in the LTspice simulations. The preliminary simulation results are also presented. The simulations fairly agree with the beam test results.
Kondo, Yasuhiro; Hirano, Koichiro; Ito, Takashi; Kikuzawa, Nobuhiro; Kitamura, Ryo; Morishita, Takatoshi; Oguri, Hidetomo; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Shinozaki, Shinichi; Shinto, Katsuhiro; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1350, p.012077_1 - 012077_7, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:52.28(Physics, Particles & Fields)We have upgraded a 3-MeV linac at J-PARC. The ion source is same as the J-PARC linac's, and the old 30-mA RFQ is replaced by a spare 50-mA RFQ, therefore, the beam energy is 3 MeV and the nominal beam current is 50 mA. The main purpose of this system is to test the spare RFQ, but also used for testing of various components required in order to keep the stable operation of the J-PARC accelerator. The accelerator has been already commissioned, and measurement programs have been started. In this paper, present status of this 3-MeV linac is presented.
Otani, Masashi*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Miyao, Tomoaki*; Liu, Y.*; Hirano, Koichiro; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Miura, Akihiko; Oguri, Hidetomo
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1350, p.012078_1 - 012078_5, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:52.28(Physics, Particles & Fields)The Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) linac is operated with design peak current of 50 mA from 2018. For operation with such a high beam current, itis important to understand transverse and longitudinal beam properties especially in low-velocity region. A medium energy beam transport (MEBT1) line between the 3-MeV radio-frequency quadrupole linac (RFQ) and the 50-MeV drift-tube linac (DTL) is a 3-m-long transport line to match the beam to the DTL and produce a macro pulse configuration for a 3-GeV rapid-cycling synchrotron (RCS). In this paper, recent measurements and beam tuning results in MEBT1 will be presented.
Nakazawa, Yuga*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Iwata, Yoshiyuki*; Iwashita, Yoshihisa*; Otani, Masashi*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Mibe, Tsutomu*; Yamazaki, Takayuki*; Yoshida, Mitsuhiro*; Kitamura, Ryo; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1350, p.012054_1 - 012054_7, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:92.41(Physics, Particles & Fields)An inter-digital H-mode drift-tube linac (IH-DTL) is developed in a muon linac at the J-PARC E34 experiment. IH-DTL will accelerate muons from 0.34 MeV to 4.5 MeV at a drive frequency of 324 MHz. Since IH-DTL adopts an APF method, with which the beam is focused in the transverse direction using the rf field only, the proper beam matching of the phase-space distribution is required before the injection into the IH-DTL. Thus, an IH-DTL prototype was fabricated to evaluate the performance of the cavity and beam transmission. As a preparation of the high-power test, tuners and coupler are designed and fabricated. In this paper, the development of the tuner and the coupler and the result of the low-power measurement will be presented.
Otani, Masashi*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Matoba, Shiro*; Mibe, Tsutomu*; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Yamazaki, Takayuki*; Hasegawa, Kazuo; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1350, p.012067_1 - 012067_6, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:73.22(Physics, Particles & Fields)Negative muonium atom ( e
e e
e , Mu
, Mu ) has unique features stimulating potential interesting for several scientific fields. Since its discovery in late 1980's in vacuum, it has been discussed that the production efficiency would be improved using a low-work function material. C12A7 was a well-known insulator as a constituent of alumina cement, but was recently confirmed to exhibit electric conductivity by electron doping. The C12A7 electride has relatively low-work function (2.9 eV). In this paper, the negative muonium production measurement with several materials including a C12A7 electride film will be presented. Measured production rate of the Mu
) has unique features stimulating potential interesting for several scientific fields. Since its discovery in late 1980's in vacuum, it has been discussed that the production efficiency would be improved using a low-work function material. C12A7 was a well-known insulator as a constituent of alumina cement, but was recently confirmed to exhibit electric conductivity by electron doping. The C12A7 electride has relatively low-work function (2.9 eV). In this paper, the negative muonium production measurement with several materials including a C12A7 electride film will be presented. Measured production rate of the Mu were 10
were 10 /s for all the Al, electride, and SUS target. Significant enhancement on electride target was not observed, thus it is presumed that the surface condition should be more carefully treated. There was no material dependence of the Mu
/s for all the Al, electride, and SUS target. Significant enhancement on electride target was not observed, thus it is presumed that the surface condition should be more carefully treated. There was no material dependence of the Mu averaged energy: it was 0.2
averaged energy: it was 0.2 0.1keV.
0.1keV.
Otani, Masashi*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Mibe, Tsutomu*; Naito, Fujio*; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Ito, Takashi; Kitamura, Ryo; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Morishita, Takatoshi; Iinuma, Hiromi*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1350, p.012097_1 - 012097_7, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:73.22(Physics, Particles & Fields)A disk and washer (DAW) coupled cavity linac (CCL) has been developed for a middle velocity part in a muon linac to measure muon anomalous magnetic moment and search for electric dipole moment. I will accelerate muons from 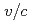 =
=  = 0.3 to 0.7 at an operational frequency of 1.3GHz. In this poster, the cavity design, beam dynamics design, and the cold-model measurements will be presented.
= 0.3 to 0.7 at an operational frequency of 1.3GHz. In this poster, the cavity design, beam dynamics design, and the cold-model measurements will be presented.
Tamura, Jun; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Morishita, Takatoshi; Naito, Fujio*; Otani, Masashi*; Nemoto, Yasuo*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1350, p.012079_1 - 012079_6, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.06(Physics, Particles & Fields)In 2013, the Annular-ring Coupled Structure (ACS) cavities were installed to the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) linac. Since then, the ACS cavities have been stably running. Although any serious problem induced by the RF window had not yet observed, we decided to replace the RF window of one ACS cavity by the newly manufactured one. The major motivations of the replacement are to check the surface condition of the RF window which have been under operation for nearly five years, to confirm that the new RF window fully meets specifications, and to learn how much time is required for high-power conditioning of the new RF window. By making use of the summer maintenance period of 2018, we carried out the replacement. This was the first experience for us to replace the RF window installed to the ACS cavity in the linac accelerator tunnel. As for the removed RF window, there was no any abnormal warning found with the visual examination. At the resuming of the cavity operation after the maintenance period, we conducted the high-power conditioning in a measured manner. It took around fifty hours so that the targeted peak power was stably input to the cavity through the new RF window. The ACS cavity with the new RF window is now stably operating.
Tamura, Jun; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Morishita, Takatoshi; Naito, Fujio*; Otani, Masashi*; Nemoto, Yasuo*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1350, p.012080_1 - 012080_6, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.06(Physics, Particles & Fields)In the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) linac, negative hydrogen beams are accelerated from 190 MeV to 400 MeV by Annular-ring Coupled Structure (ACS) cavities. The RF input coupler of the ACS21 cavity, which is the twenty-first (the last) accelerating cavity in the order of beam acceleration, had a comparatively larger Voltage Standing Wave Ratio (VSWR) value than the other ACS cavities. Therefore, we designed and manufactured a rectangular waveguide which has a capacitive iris to adjust the coupling factor of the ACS21 cavity. By making use of the summer maintenance period in 2018, we installed the newly manufactured waveguide to the cavity. Consequently, the VSWR of the ACS21 was successfully decreased to the target value which leads to the critical coupling under the nominal accelerating condition with 50-mA peak beam current.
Kamiya, Junichiro; Kotoku, Hirofumi; Shobuda, Yoshihiro; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Yamamoto, Kazami; Yanagibashi, Toru*; Horino, Koki*; Miki, Nobuharu*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1350, p.012172_1 - 012172_7, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.06(Physics, Particles & Fields)One of the issues in the J-PARC 3 GeV rapid cycling synchrotron is the high residual radiation dose around the beam injection point. A radiation shield is necessary to reduce radiation exposure of workers when maintenance is performed there. A space to install the radiation shield should be secured by newly designing a structure of the vacuum chamber at the injection point and the alumina ceramics beam pipes for the shift bump magnets. To make the space for the shield, the chamber is lengthened along the beam line and the cross-sectional shape is changed from circle to rectangle. The displacement and inner stress of the vacuum chamber due to atmospheric pressure were evaluated to be enough small by the calculation. For the ceramics beam pipe's rf-shield, the damping resistor was effective to reduce the induced modulation voltages by the pulsed magnetic field.
Moriya, Katsuhiro; Harada, Hiroyuki; Liu, Y.*; Otani, Masashi*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1350, p.012140_1 - 012140_5, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.06(Physics, Particles & Fields)Kitamura, Ryo; Hayashi, Naoki; Hirano, Koichiro; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Moriya, Katsuhiro; Oguri, Hidetomo; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Miyao, Tomoaki*; Otani, Masashi*; Kosaka, Satoshi*; et al.
Proceedings of 10th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '19) (Internet), p.2543 - 2546, 2019/06
A bunch shape monitor (BSM) is one of the important instruments to measure the longitudinal phase space distribution. For example in the J-PARC linac, three BSMs using the tungsten wire are installed at the ACS section to measure the bunch shapes between the accelerating cavities. However, this conventional BSM is hard to measure the bunch shape of H beam with 3 MeV at the beam transport between the RFQ and DTL sections, because the wire is broken around the center region of the beam. The new BSM using the carbon-nano-tube (CNT) wire is being developed to be able to measure the bunch shape of the H
beam with 3 MeV at the beam transport between the RFQ and DTL sections, because the wire is broken around the center region of the beam. The new BSM using the carbon-nano-tube (CNT) wire is being developed to be able to measure the bunch shape of the H beam with 3 MeV. The careful attention should be paid to apply the high voltage of
beam with 3 MeV. The careful attention should be paid to apply the high voltage of  10 kV to the CNT wire. The several measures are taken to suppress the discharge from the wire and operate the CNT-BSM. This presentation reports the current status of the development and future prospective for the CNT-BSM.
10 kV to the CNT wire. The several measures are taken to suppress the discharge from the wire and operate the CNT-BSM. This presentation reports the current status of the development and future prospective for the CNT-BSM.
Yamada, Ippei; Ogiwara, Norio*; Hikichi, Yusuke*; Kamiya, Junichiro; Kinsho, Michikazu
Proceedings of 10th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '19) (Internet), p.2567 - 2570, 2019/06
no abstracts in English
Hotchi, Hideaki; Harada, Hiroyuki; Takayanagi, Tomohiro
Proceedings of 10th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '19) (Internet), p.2009 - 2012, 2019/06
Yamamoto, Kazami; Kamiya, Junichiro
Proceedings of 10th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '19) (Internet), p.2020 - 2023, 2019/06
The 3 GeV rapid cycling synchrotron (RCS) at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) provides more than 500 kW beams to the Material and Life Science Experimental Facility and Main Ring synchrotron. In such a high-intensity hadron accelerator, even losing less than 0.1% of the beam can cause many problems. Such lost protons can cause serious radio-activation and accelerator component malfunctions. Therefore, we have conducted a beam study to achieve high-power operation with less loss. In addition, we have also maintained the accelerator components to enable stable operation. This paper reports the status of the J-PARC RCS over the last Japan fiscal year.
Takahashi, Hiroki; Hatakeyama, Shuichiro; Sawabe, Yuki; Miyao, Tomoaki*; Ishiyama, Tatsuya*; Suzuki, Takahiro*
Proceedings of 10th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '19) (Internet), p.3886 - 3889, 2019/06
At the J-PARC Linac, beam conditioning and study are performed using beam dumps (BDs). To be a partition with the high vacuum section, a beam window (material Ni, 0.38 mm thick, mirror-shape) is installed upstream of the BD along the beam line. Beams that can be accepted by the beam window are about 1/50 or less of rated beam according to thermal evaluation and experience. Therefore, when using a beam dump, it is necessary not to exceed this tolerance. In a 2018 beam study, the beam e that exceeded tolerance was incident on the 0-degree dump due to human error, and the beam window was cracked. Then, this has revealed the need for protection of the beam window by hardware. Therefore, based on the existing system for monitoring the per-hour beam amount, we began to develop a system to monitor one shot beam and one second beam amount. And, we succeeded in implementing a system that protects the beam window by monitoring the beam in a short time (one shot, and for one second). In addition, the performance tests using actual beams were performed, and it was confirmed that the developed system had sufficient performance requirements to protect the beam window.